
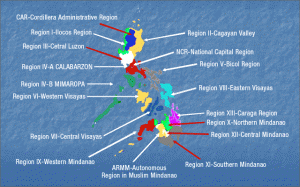
The 1987 Constitution defines the Philippines as being a unitary state, centralized around the capital of Manila. The result has been that most economic opportunities and opportunities for quality education and self-development are concentrated around the National Capital Region, and leaving the countryside, the provinces, and other cities relatively underdeveloped. As such, ordinary Filipinos seeking higher education or better job opportunities are forced to flock to Metropolitan Manila in order to try their luck, unfortunately resulting in the massive population congestion, higher pollution levels, sub-standard living conditions, extreme traffic jams, and high crime rate of Metro Manila. It has also caused the Philippine provinces to have to remit most of their taxes to the capital, and after aggregating the entire amount at the national level, smaller amounts are redistributed back to the local entities, giving them little incentive to develop their own local economies as whatever they produce does not exactly go straight to their own development and instead is mostly remitted back to the capital. By allowing for evolving region-based decentralization, the different regions in the Philippines will be better empowered to take control of their own economic decision-making, giving them greater incentives to develop their economies, attract their own investors, and create local opportunities that would allow their own people to prosper while staying in their own regions without needing to migrate to the National Capital Region. Empowering the regions this way also respects the cultures, traditions, and languages of the different ethnicities found in the different regions as this devolution of powers will allow the different regions to protect their own local cultural and/or linguistic heritage. Watch this video that talks about the concept.
Academic Papers & PDFs on Federalism:
























































![]()













Full Playlist of Federalism Lecture:
Individual Modules of the Federalism Lecture:

Module 0: Dr. Jan Erk: Introduction to the Course!

Module 1:1 Dr. Jan Erk: The Promises of Federalism

Module 1:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism and Decentralization part 1

Module 1:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism and Decentralization part 2

Module 1:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Federalism and Decentralization Reflections and Implications

Module 2:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Self Rule and Shared Rule

Module 2:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Distribution of Power

Module 2:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Multiple Identities

Module 2:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Foundational Issues

Module 2:5 Dr. Jan Erk: Weekly chat Modules 1 and 2 A message from beautiful South Africa

Module 3:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Legal Foundations

Module 3:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Political Foundations

Module 3:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Socio Economic and Socio Demographic Foundations

Module 3:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Three Scholarly Angles

Module 4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview

Module 4:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in South Africa

Module 4:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in Ethiopia

Module 4:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in Nigeria

Module 4:4 Extra video Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Assefa Fiseha

Module 5.1 Dr. Jan Erk: Decentralization in Africa

Module 5.2 Dr. Jan Erk: Economic Development and Decentralization

Module 5.3 Dr. Jan Erk: Unintended Consequences

Module 5.4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview

Module 5:5 Extra video: Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Nico Steytler

Module 6.1 Dr. Jan Erk: State Capacity

Module 6.2 Dr. Jan Erk: Imported Institutional Blueprints vs Local Solutions

Module 6.3 Dr. Jan Erk: International Involvement

Module 6:4 Extra video chat with Dr. Jan Erk

Module 6:5 Extra video Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Shawn Houlihan
Module 0: Dr. Jan Erk: Introduction to the Course!
Module 1:1 Dr. Jan Erk: The Promises of Federalism
Module 1:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism and Decentralization part 1
Module 1:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism and Decentralization part 2
Module 1:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Federalism and Decentralization Reflections and Implications
Module 2:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Self Rule and Shared Rule
Module 2:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Distribution of Power
Module 2:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Multiple Identities
Module 2:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Foundational Issues
Module 2:5 Dr. Jan Erk: Weekly chat Modules 1 and 2 A message from beautiful South Africa
Module 3:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Legal Foundations
Module 3:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Political Foundations
Module 3:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Socio Economic and Socio Demographic Foundations
Module 3:4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview of Three Scholarly Angles
Module 4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview
Module 4:1 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in South Africa
Module 4:2 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in Ethiopia
Module 4:3 Dr. Jan Erk: Federalism in Nigeria
Module 4:4 Extra video Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Assefa Fiseha
Module 5.1 Dr. Jan Erk: Decentralization in Africa
Module 5.2 Dr. Jan Erk: Economic Development and Decentralization
Module 5.3 Dr. Jan Erk: Unintended Consequences
Module 5.4 Dr. Jan Erk: Overview
Module 5:5 Extra video: Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Nico Steytler
Module 6.1 Dr. Jan Erk: State Capacity
Module 6.2 Dr. Jan Erk: Imported Institutional Blueprints vs Local Solutions
Module 6.3 Dr. Jan Erk: International Involvement
Module 6:4 Extra video chat with Dr. Jan Erk
Module 6:5 Extra video Dr. Jan Erk Interview with Shawn Houlihan
Forum of Federations Basic Lectures:

Module 1: Why is Federalism important to the World?

Module 2: How do Federal Countries work and do they work the same?

Module 3: How does the central government define and shape a country?

Module 4: Why are constitutions important to effective federal governance?

Module 5: How do Federal Countries organize the raising, sharing, and spending of money?

Module 6: How the Central Governments and Subnational Governments work together in Federalism

Module 7: How do Federal Countries balance Unity and Diversity?
Learning about Fiscal Federalism Part 1

Learning about Fiscal Federalism Part 2

Decentralization 1: Why central and local governments are both necessary

Decentralization 2: The South African Way

Decentralization 3: Switzerland

Decentralization 4: The Canadian Way

Decentralization 5: Tunisia, towards Decentralization

The Quest for Federalism in Nepal
Module 1: Why is Federalism important to the World?
Module 2: How do Federal Countries work and do they work the same?
Module 3: How does the central government define and shape a country?
Module 4: Why are constitutions important to effective federal governance?
Module 5: How do Federal Countries organize the raising, sharing, and spending of money?
Module 6: How the Central Governments and Subnational Governments work together in Federalism
Module 7: How do Federal Countries balance Unity and Diversity?
Learning about Fiscal Federalism Part 1
Learning about Fiscal Federalism Part 2
Decentralization 1: Why central and local governments are both necessary
Decentralization 2: The South African Way
Decentralization 3: Switzerland
Decentralization 4: The Canadian Way
Decentralization 5: Tunisia, towards Decentralization
The Quest for Federalism in Nepal
Ashutosh Varshney Lectures on Ethnic Conflict:
-

-
1: Ethnicity & Nationalism
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
2: Civilisation & Nationalism
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
3: Ethnicity & Class
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
4: Conflict & Violence
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
5: Essentialism & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
6: Instrumentalism & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
7: Micro-foundation of Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
8: Constructivism, Modernity, & Identities
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
9: Rise of Nationalism in Britain & France
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
10: Postmodernism & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
11: Facts & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
12: Institutions & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
13: Consociational Democracy & Ethnic Conflict
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
14: Hindu-Muslim Riots in India
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
15: Local Concentration of Riots & Civil Society
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
16: Civil Wars
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
17: Institutions & Identities
-
Watch Video
-
-

-
18: Liberalism, Nationalism & Ethnic Rights
-
Watch Video
-


 Learning about Federalism using Australia’s example
Learning about Federalism using Australia’s example Forum of Federations: Videos for Learning about Federalism
Forum of Federations: Videos for Learning about Federalism Constitutional Reform First before claiming Sabah!
Constitutional Reform First before claiming Sabah! Why Do So Many Filipinos Misunderstand System Change?
Why Do So Many Filipinos Misunderstand System Change? Federalism & Decentralization: Evaluating Africa’s Track Record
Federalism & Decentralization: Evaluating Africa’s Track Record Frequently Asked Questions (Tagalog)
Frequently Asked Questions (Tagalog) Federalism in Africa: The Case of Ethiopia – Challenges & Prospects
Federalism in Africa: The Case of Ethiopia – Challenges & Prospects Rediscovering the Advantages of Federalism
Rediscovering the Advantages of Federalism How does Federalism work?
How does Federalism work? Rizal the Federalist; Bonifacio the Unitarian
Rizal the Federalist; Bonifacio the Unitarian Tacloban Tragedy: A Painful Wake-up Call
Tacloban Tragedy: A Painful Wake-up Call Ang Hagupit ng Bagyong Yolanda
Ang Hagupit ng Bagyong Yolanda The Coming Fall of the “Noynoy Project”
The Coming Fall of the “Noynoy Project” Infographic: Solutions to the Root Causes of the Pork Barrel
Infographic: Solutions to the Root Causes of the Pork Barrel Nápoles & Pork Barrel: It’s the Lousy System
Nápoles & Pork Barrel: It’s the Lousy System Polls aren’t just for Metro Manila: Why Federalism?
Polls aren’t just for Metro Manila: Why Federalism? It’s all about Competition
It’s all about Competition Let’s Talk Basketball – by Figo Cantos
Let’s Talk Basketball – by Figo Cantos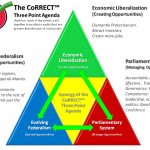 The CoRRECT™ Three Point Agenda
The CoRRECT™ Three Point Agenda

















 I believe: This is a CoRRECT™ Video with a very positive message
I believe: This is a CoRRECT™ Video with a very positive message Walang Natira: Gloc-9's MTV Rap about the OFW Phenomenon
Walang Natira: Gloc-9's MTV Rap about the OFW Phenomenon